Abstract
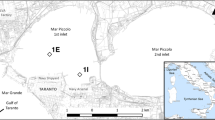
Porewater concentrations and benthic fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), sulfate (SO4 2−), calcium (Ca2+), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), ammonia (NH4 +), and soluble reactive phosphorus (DIP) were measured in the sediments of Albufera d’Es Grau (Minorca Island), a mesohaline lagoon, in Spring/early Summer. In this period, DIC and NH4 + were produced in sediments by the decomposition of organic matter through aerobic pathways in the upper 1 cm and below this depth through anaerobic pathways mainly sulfate reduction. In March, the average flux of DIC into the water was 21.45±26.05 mmol m−2 d−1, more than 50% of which came from anaerobic respiration below 1 cm sediment depth. In June, the DIC flux increased to 55.29±24.38 mmol m−2 d−1, but the rates of production through sulfate reduction decreased drastically to less than 10% of the total flux. NH4 +-flux was also relatively low, decreasing from 1000 μmol m−2 d−1 in March to 200 μmol m−2 d−1 in June. Differences between stoichiometric relationships in porewater and in measured fluxes indicated immobilization of nitrogen in sediments due to macrophyte uptake and nitrification, this immobilization mainly occurring in early summer. DIP release into the water was always below 15 μmol m−2 d−1, these low values being attributed to three main factors: a) more than 40% of sedimentary phosphorus in Es Grau sediments occurred in non-reactive forms such as detrital apatite or refractory-P; b) accumulation of Fe-oxides at the sediment surface acts as a trap for DIP produced through organic matter decomposition in March; and c) phosphate released from Fe-bound P in June during the period of increased oxygen consumption was effectively trapped as fulvic-P complexes and as microbial phosphate. Differences between fluxes directly measured and estimated from porewater concentrations also indicated that, at some sites, bioturbation contributed to the total flux of NH4 + and Mn and phosphate immobilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aller, R. C. 1994. Bioturbation and remineralization of sedimentary organic matter: Effects of redox oscillation. Chemical Geology 114:331–345.
Aller, R. C. and J. Y. Aller. 1998. The effect of biogenic irrigation intensity and solute exchange on diagenetic reaction rates in marine sediments. Journal of Marine Research 56:905–936.
Aller, R. C. and J. E. Mackin. 1989. Open incubation, diffusion methods for measuring solute reaction rates in sediments. Journal of Marine Research 47:411–440.
Aller, R. C., J. E. Mackin, and R. T. Cox. 1986. Diagenesis of Fe and S in Amazon inner shelf muds: apparent dominance of Fe reduction and implications for the genesis of iron-stones. Continental Shelf Research 6:263–289.
Andersen, F. O. and H. S. Jensen. 1992. Regeneration of inorganic phosphorus and nitrogen from decomposition of seston in a freshwater sediment. Hydrobiologia 228:71–81.
Atkinson, M. J. and S. V. Smith. 1983. C:N:P ratios of benthic marine plants. Limnology and Oceanography 28:568–574.
Barbanti, A., V. U. Ceccherelli, F. Frascari, G. Reggiani, and G. Rosso. 1992. Nutrient regeneration processes in bottom sediments in a Po delta lagoon Italy and the role of bioturbation in determining the fluxes at the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 228:1–21.
Bartoli, M., M. Cattadori, G. Giordani, and P. Viaroli. 1996. Benthic oxygen respiration, ammonium and phosphorus regeneration in surficial sediments of the Sacca di Goro Northern Italy and two french coastal lagoons, a comparative study. Hydrobiologia 329:143–159.
Berner, R. A. 1977. Stoichiometric model for nutrient regeneration in anoxic sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 22:781–786.
Bertuzzi, A., J. Faganeli, C. Welker, and A. Brambati. 1997. Benthic fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon, nutrients and oxygen in the Gulf of Trieste Northern Adriatic. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 99:305–314.
Billen, G., C. Lancelot, and M. Meybeck. 1991. N, P, and Si retention along the aquatic continuum from land to ocean. p. 199–244. In C. Mantoura, J. M. Martin, and R. Wollast (eds.) Ocean Margin Processes in Global Change. Wiley and Sons, Chichester, UK.
Canfield, D. E. 1993. Organic matter oxidation in marine sediments. p. 333–363. In R. Wollast, L. Chou and F. Mackenzie (eds.) Interactions of C, N, P and S. Biogeochemical Cycles. North Atlantic Treaty Organization Advanced Research Workshop, Berlin, Germany.
Caracco, N. F., J. J. Cole, and G. E. Likens. 1989. Evidence for sulphate controlled phosphorus release from sediments in aquatic systems. Nature 341:316–318.
Caracco, N. F., J. J. Cole, and G. E. Likens. 1993. Sulfate control of phosphorus avilability in lakes. Hydrobiologia 253:275–280.
Cermelj, B., A. Bertuzzi, and J. Faganeli. 1997. Modelling of pore water nutrient distribution and benthic fluxes in shallow coastal waters Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 99:435–443.
Ciceri, G., S. Ceradini, and A. Zitelli. 1999. Nutrient benthic fluxes and pore water profiles in a shallow brackish marsh of the lagoon of Venice. Analitica di Chimica 89:359–375.
Conley, D. J., W. M. Smith, J. C. Cornwell, and T. R. Fisher. 1995. Transformations of particle-bound phosphorus at the land-sea interface. Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 40:161–176.
Gachter, R. and J. S. Meyer. 1993. The role of microorganisms in mobilization and fixation of phosphorus in sediments. Hydrobiologia 253:103–121.
Golterman, H. L. 1977. Sediment as a source of phosphate for algal growth. p. 286–293. In H. L. Golterman. (ed.) Interactions between Sediments and Freshwater. Junk, The Hague, Netherlands.
Golterman, H. L. 1998. The distribution of phosphate over iron-bound and calcium-bound phosphate in stratified sediments. Hydrobiologia 364:75–81.
Golterman, H. L. 2001. Fractionation and bioavailability of phosphates in lacustrine sediments: a review. Limnetica 20:15–29.
Gomez-Parra, A. and J. M. Forja. 1993. Benthic nutrient fluxes in Cadiz Bay SW Spain. Hydrobiologia 252:23–34.
Grasshoff, K., M. Ehrhardt, and K. Kremling. 1983. Methods of Sea Water Analysis. Verlag Chimie, Weinheim, Germany.
Hammond, D. E., C. Fuller, D. Harmon, B. Hartman, M. Korosec, L. G. Miller, R. Rea, S. Warren, W. Berelson, and S. W. Hager. 1985. Benthic fluxes in San Francisco Bay. Hydrobiologia 129:69–90.
Jahnke, R. A., D. B. Craven, and J-F. Gaillard. 1994. The influence of organic matter diagenesis on CaCO3 dissolution at the deep-sea floor. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 58:2799–2809.
Jahnke, R. A. and D. B. Jahnke. 2000. Rates of C, N, P and Si recycling and denitrification at the US Mid-Atlantic continental slope depocenter. Deep-Sea Research 47:1405–1428.
Jensen, H. S., K. J. Mcglathery, R. Marino, and R. W. Howarth. 1998. Forms and availability of sediment phosphorus in carbonate sand of Bermuda seagrass beds. Limnology and Oceanography 43:799–810.
Jensen, H. S., P. B. Mortensen, F. O. Andersen, E. Rasmusen, and A. Jensen. 1995. Phosphorus cycling in a coastal marine sediment, Aarhus Bay, Denmark. Limnology and Oceanography 40:908–917.
Jorgensen, B. B. 1982. Mineralization of organic matter in the sea bed-the role of sulfate reduction. Nature 296:643–645.
Joye, S. B., T. L. Connell, L. G. Miller, R. S. Oremland, and R. S. Jellison. 1999. Oxidation of ammonia and methane in an alkaline, saline lake. Limnology and Oceanography 44:178–188.
Kleeberg, A. 1997. Interactions between benthic phosphorus release and sulfur cycling in lake Scharmützelsee (Germany). Water, Air and Soil Pollution 99:391–399.
Li, Y. and S. Gregory. 1974. Diffusion of ions in seawater and in deep-sea sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 38:703–714.
López, P. 2003. Effect of changes in water salinity on ammonium, calcium and dissolved inorganic carbon water/sediment dynamics. Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 56:943–956.
López, P. 2004. Spatial distribution of sedimentary P pools in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon “Albufera d’Es Grau” (Minorca island, Spain). Marine Geology 203:161–176.
López, P., X. Lluch, M. Vidal, and J. A. Morguí. 1996. Adsorption of phosphorus on sediments of the Balearic Islands Spain related to their composition. Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 42:185–196.
López, P. and J. A. Morguí. 1992. Phosphate and calcium saturation in a stratified coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 228:55–63.
López, P., J. A. Morguí, M. Vidal, and X. Lluch. 2001. Pore-water composition and alkalinity balance in sediments of a meromictic coastal lagoon Cibollar, Majorca, Spain. Verhein International verein. Limnology 27:3389–3393.
López, P., M. Vidal, X. Lluch, and J. A. Morguí. 1995. Sediment metabolism in a transitional continental/marine area: The Albufera of Majorca (Balearic Islands, Spain). Marine and Freshwater Research 46:45–53.
Lovley, D. R. and M. J. Klug. 1986. Model for the distribution of sulfate reduction and methanogenesis in freshwater sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 50:11–18.
Millero, F. 1995. Thermodynamics of the carbon dioxide system in the oceans. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 59:661–677.
Morell, J. M. and J. E. Corredor. 1993. Sediment nitrogen trapping in a mangrove lagoon. Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 37:203–212.
Nixon, S. W. 1981. Remineralisation and nutrients cycling in coastal marine ecosystems. p. 111–138. In B. J. Neilson and L. E. Cronin (eds.) Estuaries and Nutrients. Humana, Clifton, NJ, USA.
Pretus, J. L. 1989. Limnología de la Albufera de Menorca Menorca, España. Limnetica 5:69–81.
Rosenfeld, J. K. 1979. Ammonium adsorption in nearshore anoxic sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 24:356–364.
Rysgaard, S. and P. Berg. 1996. Mineralization in a northeastern Greenland sediment, mathematical modelling, measured sediment porewater profiles and actual activities. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 11:297–305.
Rysgaard, S., P. Thastum, T. Dalsgaard, P. B. Christensen, and N. P. Sloth. 1999. Effects of salinity on NH4 + adsorption capacity, nitrification, and denitrification in Danish estuarine sediments. Estuaries 22:21–30.
Slomp, C. P., J. F. P. Malschaert, and W. Van Raaphorst. 1998. The role of adsorption in sediment-water exchange of phosphate in North Sea continental margin sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 43:832–846.
Spagnoli, F. and M. C. Bergamini. 1997. Water-sediment exchange of nutrients during early diagenesis and resuspension of anoxic sediments from the Northern Adriatic Sea shelf. Water, Air and Soil Pollution 99:541–556.
Stumm, W. and J. J. Morgan. 1981. Aquatic Chemistry, second edition. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, NY, USA.
Talling, J. F. 1973. The application of some electrochemical methods to the measurement of photosynthesis and respiration in fresh waters. Freshwater Biology 3:335–363.
Thamdrup, B. and D. E. Canfield. 1996. Pathways of carbon oxidation in continental margin sediments off central Chile. Limnology and Oceanography 41:1629–1650.
Ullman, W. J. and R. C. Aller. 1982. Diffusion coefficients in near-shore marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 27:552–556.
Ullman, W. J. and R. C. Aller. 1989. Nutrient release rates from the sediments of Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Hydrobiologia 171:127–140.
Viaroli, P., M. Bartoli, C. Bondavalli, R. R. Christian, G. Giordani, and M. Naldi. 1996. Macrophyte communities and their impact on benthic fluxes of oxygen, sulphide and nutrients in shallow eutrophic environments. Hydrobiologia 329:105–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez, P. Composition of porewater and benthic fluxes in the mesohaline Es Grau lagoon (Minorca, Spain) during spring and early summer. Wetlands 24, 796–810 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2004)024[0796:COPABF]2.0.CO;2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2004)024[0796:COPABF]2.0.CO;2